Software Testing Quick Guide. Software Testing Quick Guide. Software Testing Overview. What is Testing Testing is the process of evaluating a system or its components with the intent to find whether it satisfies the specified requirements or not. In simple words, testing is executing a system in order to identify any gaps, errors, or missing requirements in contrary to the actual requirements. According to ANSIIEEE 1. Testing can be defined as A process of analyzing a software item to detect the differences between existing and required conditions that is defectserrorsbugs and to evaluate the features of the software item. Who does Testing It depends on the process and the associated stakeholders of the projects. In the IT industry, large companies have a team with responsibilities to evaluate the developed software in context of the given requirements. Black Box Testing Example Software Project' title='Black Box Testing Example Software Project' />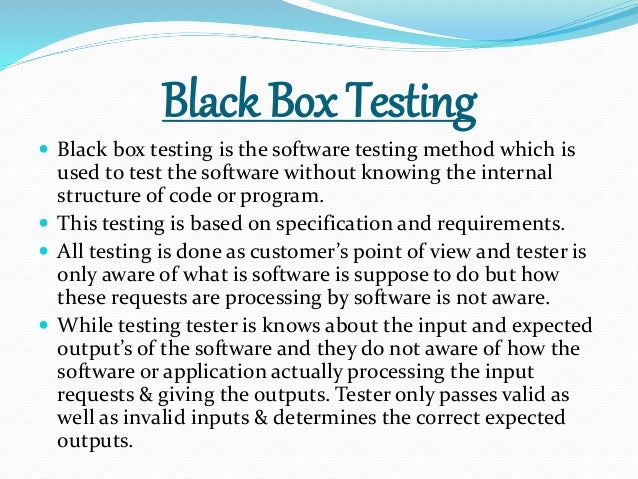 Moreover, developers also conduct testing which is called Unit Testing. In most cases, the following professionals are involved in testing a system within their respective capacities Software Tester. Software Developer. Project LeadManager. End User. Different companies have different designations for people who test the software on the basis of their experience and knowledge such as Software Tester, Software Quality Assurance Engineer, QA Analyst, etc. It is not possible to test the software at any time during its cycle. The next two sections state when testing should be started and when to end it during the SDLC. When to Start Testing An early start to testing reduces the cost and time to rework and produce error free software that is delivered to the client. Altom, in collaboration with Kaner, Fiedler Associates, LLC, is offering a new generation of BlackBox Software Testing courses BBST 3. What is White Box Testing White Box Testing is the testing of a software solutions internal coding and infrastructure. It focuses primarily on strengthening. Wwe Tlc Full Match Download Yahoo. Software Testing An overview Introduction Fundamentals What is Software Testing Why testing is necessary Who does the testing What has to be testedHowever in Software Development Life Cycle SDLC, testing can be started from the Requirements Gathering phase and continued till the deployment of the software. It also depends on the development model that is being used. For example, in the Waterfall model, formal testing is conducted in the testing phase but in the incremental model, testing is performed at the end of every incrementiteration and the whole application is tested at the end. Testing is done in different forms at every phase of SDLC During the requirement gathering phase, the analysis and verification of requirements are also considered as testing. Software testing is an investigation conducted to provide stakeholders with information about the quality of the software product or service under test. Software. Regression Testing Software Testing Basics TEST PLAN Fundamentals TEST PLAN DEFINITION A Software Test Plan is a document describing the testing scope and activities. What is Black Box Testing Black box testing is a software testing techniques in which functionality of the software under test SUT is tested without looking at the. Reviewing the design in the design phase with the intent to improve the design is also considered as testing. Testing performed by a developer on completion of the code is also categorized as testing. When to Stop Testing It is difficult to determine when to stop testing, as testing is a never ending process and no one can claim that a software is 1. The following aspects are to be considered for stopping the testing process Testing Deadlines. Completion of test case execution. Completion of functional and code coverage to a certain point. Bug rate falls below a certain level and no high priority bugs are identified. Management decision. Verification Validation. These two terms are very confusing for most people, who use them interchangeably. The following table highlights the differences between verification and validation. S. N. Verification. Validation. 1Verification addresses the concern Are you building it rightValidation addresses the concern Are you building the right thing2. Ensures that the software system meets all the functionality. Ensures that the functionalities meet the intended behavior. Verification takes place first and includes the checking for documentation, code, etc. Validation occurs after verification and mainly involves the checking of the overall product. Done by developers. Done by testers. 5. It has static activities, as it includes collecting reviews, walkthroughs, and inspections to verify a software. It has dynamic activities, as it includes executing the software against the requirements. It is an objective process and no subjective decision should be needed to verify a software. It is a subjective process and involves subjective decisions on how well a software works. Software Testing Myths. Given below are some of the most common myths about software testing. Myth 1 Testing is Too Expensive. Reality There is a saying, pay less for testing during software development or pay more for maintenance or correction later. Early testing saves both time and cost in many aspects, however reducing the cost without testing may result in improper design of a software application rendering the product useless. Myth 2 Testing is Time Consuming. Reality During the SDLC phases, testing is never a time consuming process. However diagnosing and fixing the errors identified during proper testing is a time consuming but productive activity. Myth 3 Only Fully Developed Products are Tested. Reality No doubt, testing depends on the source code but reviewing requirements and developing test cases is independent from the developed code. However iterative or incremental approach as a development life cycle model may reduce the dependency of testing on the fully developed software. Myth 4 Complete Testing is Possible. Reality It becomes an issue when a client or tester thinks that complete testing is possible. It is possible that all paths have been tested by the team but occurrence of complete testing is never possible. There might be some scenarios that are never executed by the test team or the client during the software development life cycle and may be executed once the project has been deployed. Myth 5 A Tested Software is Bug Free. Reality This is a very common myth that the clients, project managers, and the management team believes in. No one can claim with absolute certainty that a software application is 1. Myth 6 Missed Defects are due to Testers. Reality It is not a correct approach to blame testers for bugs that remain in the application even after testing has been performed. This myth relates to Time, Cost, and Requirements changing Constraints. However the test strategy may also result in bugs being missed by the testing team. Myth 7 Testers are Responsible for Quality of Product. Reality It is a very common misinterpretation that only testers or the testing team should be responsible for product quality. Testers responsibilities include the identification of bugs to the stakeholders and then it is their decision whether they will fix the bug or release the software. Releasing the software at the time puts more pressure on the testers, as they will be blamed for any error. Myth 8 Test Automation should be used wherever possible to Reduce Time. Reality Yes, it is true that Test Automation reduces the testing time, but it is not possible to start test automation at any time during software development. Test automaton should be started when the software has been manually tested and is stable to some extent. Moreover, test automation can never be used if requirements keep changing. Myth 9 Anyone can Test a Software Application. Reality People outside the IT industry think and even believe that anyone can test a software and testing is not a creative job. However testers know very well that this is a myth. Thinking alternative scenarios, try to crash a software with the intent to explore potential bugs is not possible for the person who developed it. Myth 1. 0 A Testers only Task is to Find Bugs. Reality Finding bugs in a software is the task of the testers, but at the same time, they are domain experts of the particular software. Developers are only responsible for the specific component or area that is assigned to them but testers understand the overall workings of the software, what the dependencies are, and the impacts of one module on another module. Software Testing QA, QC Testing. Testing, Quality Assurance, and Quality Control. Most people get confused when it comes to pin down the differences among Quality Assurance, Quality Control, and Testing.
Moreover, developers also conduct testing which is called Unit Testing. In most cases, the following professionals are involved in testing a system within their respective capacities Software Tester. Software Developer. Project LeadManager. End User. Different companies have different designations for people who test the software on the basis of their experience and knowledge such as Software Tester, Software Quality Assurance Engineer, QA Analyst, etc. It is not possible to test the software at any time during its cycle. The next two sections state when testing should be started and when to end it during the SDLC. When to Start Testing An early start to testing reduces the cost and time to rework and produce error free software that is delivered to the client. Altom, in collaboration with Kaner, Fiedler Associates, LLC, is offering a new generation of BlackBox Software Testing courses BBST 3. What is White Box Testing White Box Testing is the testing of a software solutions internal coding and infrastructure. It focuses primarily on strengthening. Wwe Tlc Full Match Download Yahoo. Software Testing An overview Introduction Fundamentals What is Software Testing Why testing is necessary Who does the testing What has to be testedHowever in Software Development Life Cycle SDLC, testing can be started from the Requirements Gathering phase and continued till the deployment of the software. It also depends on the development model that is being used. For example, in the Waterfall model, formal testing is conducted in the testing phase but in the incremental model, testing is performed at the end of every incrementiteration and the whole application is tested at the end. Testing is done in different forms at every phase of SDLC During the requirement gathering phase, the analysis and verification of requirements are also considered as testing. Software testing is an investigation conducted to provide stakeholders with information about the quality of the software product or service under test. Software. Regression Testing Software Testing Basics TEST PLAN Fundamentals TEST PLAN DEFINITION A Software Test Plan is a document describing the testing scope and activities. What is Black Box Testing Black box testing is a software testing techniques in which functionality of the software under test SUT is tested without looking at the. Reviewing the design in the design phase with the intent to improve the design is also considered as testing. Testing performed by a developer on completion of the code is also categorized as testing. When to Stop Testing It is difficult to determine when to stop testing, as testing is a never ending process and no one can claim that a software is 1. The following aspects are to be considered for stopping the testing process Testing Deadlines. Completion of test case execution. Completion of functional and code coverage to a certain point. Bug rate falls below a certain level and no high priority bugs are identified. Management decision. Verification Validation. These two terms are very confusing for most people, who use them interchangeably. The following table highlights the differences between verification and validation. S. N. Verification. Validation. 1Verification addresses the concern Are you building it rightValidation addresses the concern Are you building the right thing2. Ensures that the software system meets all the functionality. Ensures that the functionalities meet the intended behavior. Verification takes place first and includes the checking for documentation, code, etc. Validation occurs after verification and mainly involves the checking of the overall product. Done by developers. Done by testers. 5. It has static activities, as it includes collecting reviews, walkthroughs, and inspections to verify a software. It has dynamic activities, as it includes executing the software against the requirements. It is an objective process and no subjective decision should be needed to verify a software. It is a subjective process and involves subjective decisions on how well a software works. Software Testing Myths. Given below are some of the most common myths about software testing. Myth 1 Testing is Too Expensive. Reality There is a saying, pay less for testing during software development or pay more for maintenance or correction later. Early testing saves both time and cost in many aspects, however reducing the cost without testing may result in improper design of a software application rendering the product useless. Myth 2 Testing is Time Consuming. Reality During the SDLC phases, testing is never a time consuming process. However diagnosing and fixing the errors identified during proper testing is a time consuming but productive activity. Myth 3 Only Fully Developed Products are Tested. Reality No doubt, testing depends on the source code but reviewing requirements and developing test cases is independent from the developed code. However iterative or incremental approach as a development life cycle model may reduce the dependency of testing on the fully developed software. Myth 4 Complete Testing is Possible. Reality It becomes an issue when a client or tester thinks that complete testing is possible. It is possible that all paths have been tested by the team but occurrence of complete testing is never possible. There might be some scenarios that are never executed by the test team or the client during the software development life cycle and may be executed once the project has been deployed. Myth 5 A Tested Software is Bug Free. Reality This is a very common myth that the clients, project managers, and the management team believes in. No one can claim with absolute certainty that a software application is 1. Myth 6 Missed Defects are due to Testers. Reality It is not a correct approach to blame testers for bugs that remain in the application even after testing has been performed. This myth relates to Time, Cost, and Requirements changing Constraints. However the test strategy may also result in bugs being missed by the testing team. Myth 7 Testers are Responsible for Quality of Product. Reality It is a very common misinterpretation that only testers or the testing team should be responsible for product quality. Testers responsibilities include the identification of bugs to the stakeholders and then it is their decision whether they will fix the bug or release the software. Releasing the software at the time puts more pressure on the testers, as they will be blamed for any error. Myth 8 Test Automation should be used wherever possible to Reduce Time. Reality Yes, it is true that Test Automation reduces the testing time, but it is not possible to start test automation at any time during software development. Test automaton should be started when the software has been manually tested and is stable to some extent. Moreover, test automation can never be used if requirements keep changing. Myth 9 Anyone can Test a Software Application. Reality People outside the IT industry think and even believe that anyone can test a software and testing is not a creative job. However testers know very well that this is a myth. Thinking alternative scenarios, try to crash a software with the intent to explore potential bugs is not possible for the person who developed it. Myth 1. 0 A Testers only Task is to Find Bugs. Reality Finding bugs in a software is the task of the testers, but at the same time, they are domain experts of the particular software. Developers are only responsible for the specific component or area that is assigned to them but testers understand the overall workings of the software, what the dependencies are, and the impacts of one module on another module. Software Testing QA, QC Testing. Testing, Quality Assurance, and Quality Control. Most people get confused when it comes to pin down the differences among Quality Assurance, Quality Control, and Testing.